Sunburn
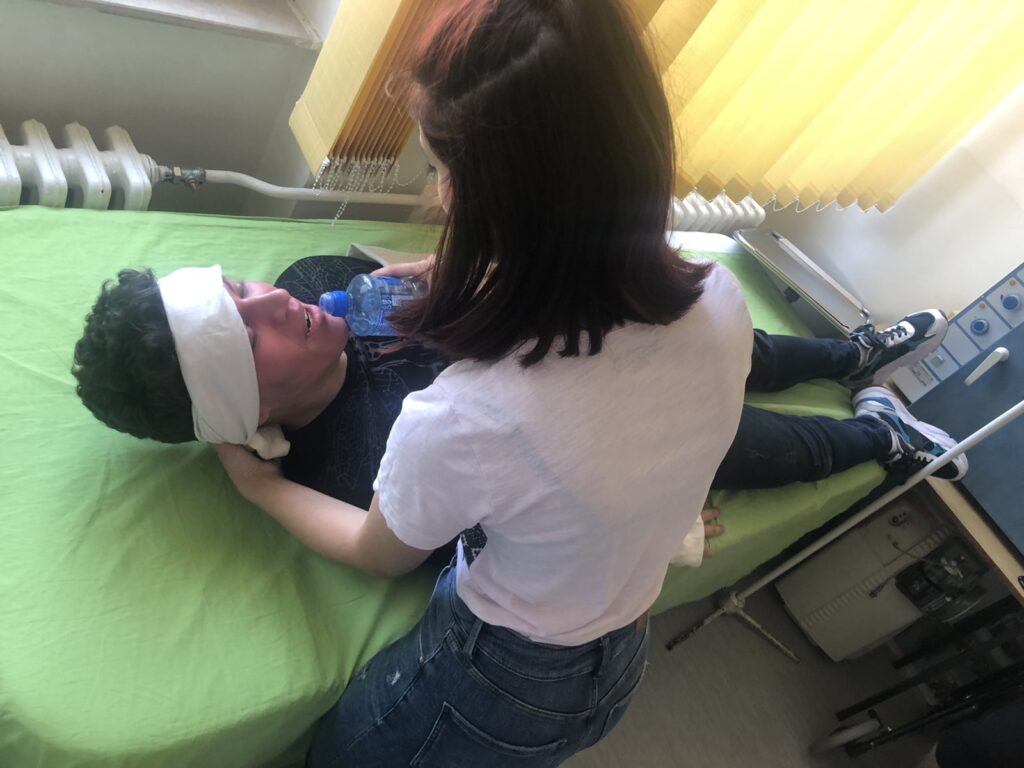
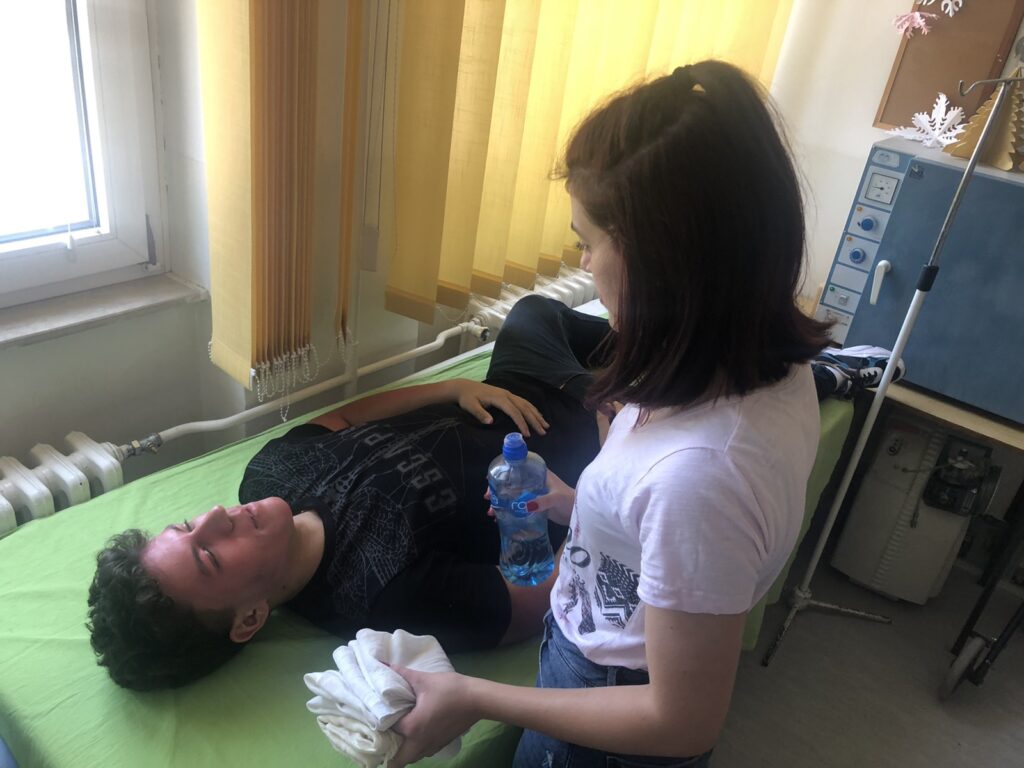

Sunburn is a thermoregulatory disorder with severe headaches, nausea and redness of the skin, which occurs after excessive exposure of the unprotected head, and especially the back of the head, to direct sunlight. As a result of sunburn, the temperature in the skull increases (as in an espresso pot), and the body tries to cool the brain by sending more and more cold blood to the head, dilating blood vessels in the brain that swell or bleed due to a sudden increase in blood vessel volume. .
The symptoms and signs of sunburn are: after a latent period lasting 6-12 hours. Dry skin and fever, headache, dizziness, nausea, rapid and weak pulse, shallow and rapid breathing, vomiting, flushing, restlessness, malaise, tinnitus and fainting occur.
First Aid
The casualty person should be immediately removed from the sun in the shade (or in a darkened, cold and ventilated room) and free of excess clothing. If the person is unconscious, lay him on his side. Then cool her head and body with a light spray of water (not a sudden splash from the bucket), put cold compresses or bags of ice around her neck, chest and wrists and legs. Stop cooling when the body temperature drops below 38 ° C. If the injured person is conscious, place him in a supine position with his legs raised, give him a small amount of cold salted water or plenty of cold natural fruit drinks to lower his body temperature and replenish fluid. The cooling of the injured person stops only when the body temperature drops below 38 ° C.
Measures to prevent sunburn are: wearing a hat, cap or a transparent straw hat with a wide brim that protects from direct sunlight. Wearing appropriate clothing, as well as avoiding prolonged exposure to the sun. If you stay in the sun for a long time, you should periodically cool your hair, head and nap with water and drink enough cold liquids.

